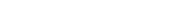George Washington Presidential $1 Coin
- Year of Issue: 2007
- Authorizing Legislation: Public Law 109–145
Background
Following the ratification of the Constitution of the United States, the Electoral College unanimously elected George Washington to serve as the United States’ first President.
The former General and Commander in Chief of the Continental Army served two terms as president, holding the office from 1789 to 1797.
On June 1, 1789, President George Washington signed the country’s first Act of Congress, concerning the administration of oaths. In 1791, President Washington presided over the Nation’s first recorded Cabinet meeting, which included Alexander Hamilton as the United States’ first Secretary of the Treasury and Thomas Jefferson as the first Secretary of State.
President Washington himself laid the cornerstone for the United States Capitol building in Washington, D.C., on September 18, 1793.
Washington also laid the groundwork for the United States’ earliest foreign policy stance when he issued his Declaration of Neutrality in 1793, a direct response to the emerging conflict between England and France.
Coinage Legislation under President George Washington
The Coinage Act of April 2, 1792 — Commonly referred to as the Mint Act, this Act establishes the United States Mint at Philadelphia, the Nation’s capital at the time. The Mint Act called for the production of the following coins, and specified their weight in gold, silver or copper: half-cent, cent, half-dime, dime, quarter-dollar, half-dollar, dollar, quarter-eagle ($2.50), half-eagle ($5.00), and eagle ($10).
Act of May 8, 1792 — This Act authorizes the Director to purchase up to 150 tons of copper for the coining of cents and half-cents.
Act of January 14, 1793 — This Act establishes the metal content of cents and half-cents.
Act of February 9, 1793 — This Act establishes foreign exchange rates, and ends the acceptance of foreign coinage (with the exception of the Spanish milled dollar) as legal tender in the United States.
Act of March 3, 1794 — This Act provides an accounting method of receiving metals for the purpose of producing coins from the metals received.
Act of March 3, 1795 — This Act establishes the positions of melter and refiner of the United States Mint and grants the President the authority to reduce the amount of copper used in both the cent and half-cent.
United States Mint Directors appointed by President Washington
1792 David Rittenhouse — First Director of the United States Mint
1795 Henry William de Saussure — Second Director
1795 Elias Boudinot — Third Director
Characteristics
Obverse Inscriptions
- GEORGE WASHINGTON
- 1ST PRESIDENT 1789-1797
Reverse Inscriptions
- UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
- $1
Incused (edge) Inscriptions
- 2007
- E PLURIBUS UNUM
- IN GOD WE TRUST
- mint mark ("P", "D," or "S")
Mint and Mint Mark
Artist Information
Obverse- Joseph Menna, Medallic Artist
- Designer: Don Everhart, Sculptor-Engraver